How to do Futures Trading on Zoomex
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the fundamentals of futures trading on Zoomex, covering key concepts, essential terminology, and step-by-step instructions to help both beginners and experienced traders navigate this exciting market.

What are Futures Contracts Trading?
Futures Trading: In the Futures market, a position opened is a Futures contract representing the value of a specific cryptocurrency. When it is opened, you do not own the underlying cryptocurrency, but a contract that you agree to buy or sell a specific cryptocurrency at some point in the future.For example, when purchasing BTC with USDT in the spot market, the acquired BTC will appear in your account’s asset list, indicating ownership and possession.
However, in the contract market, initiating a long BTC position with USDT won’t immediately reflect the purchased BTC in your Futures account. Instead, it displays the position, granting you the option to sell the BTC in the future for potential profit or loss.
Perpetual futures contracts offer traders a means to access cryptocurrency markets, yet they entail substantial risks and necessitate careful consideration before use.
-
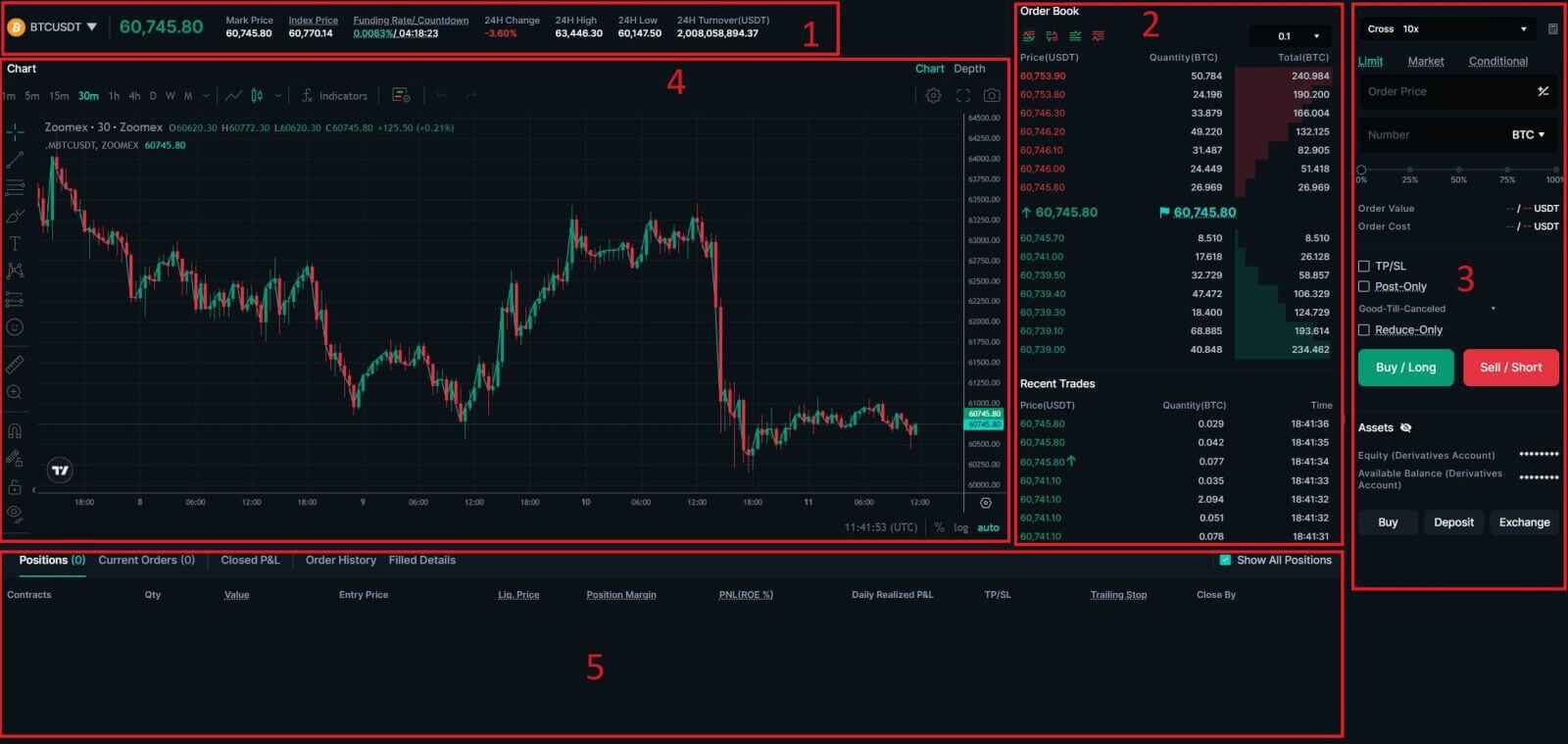
The trading volume of Spot Pairs in 24 hours:
This refers to the total volume of trading activity that has occurred within the last 24 hours for specific spot pairs (e.g., BTC/USD, ETH/BTC).
-
Order Book:
The order book displays a list of all open buy and sell orders for a particular cryptocurrency pair. It shows the current market depth and helps traders gauge supply and demand levels.
-
Buy/Sell Section:
This is where traders can place orders to buy or sell cryptocurrencies. It typically includes options for market orders (executed immediately at the current market price) and limit orders (executed at a specified price).
-
Candlestick Chart:
Candlestick charts are graphical representations of price movements over a specific period. They display opening, closing, and high, and low prices within the chosen timeframe, helping traders analyze price trends and patterns.
-
Current Orders/Order History/Trade History:
Traders can view their Current Order, Order History, and Trade History, including details such as entry price, exit price, profit/loss, and time of trade.
How to Trade BTC/USDT Perpetual Futures on Zoomex (Web)
1. Open the Zoomex website. Click on the [Derivatives] to continue.
2. Click on [USDT Perpetual] to continue.
3. Click on [BTCUSDT] to choose the trading pairs that you prefer.
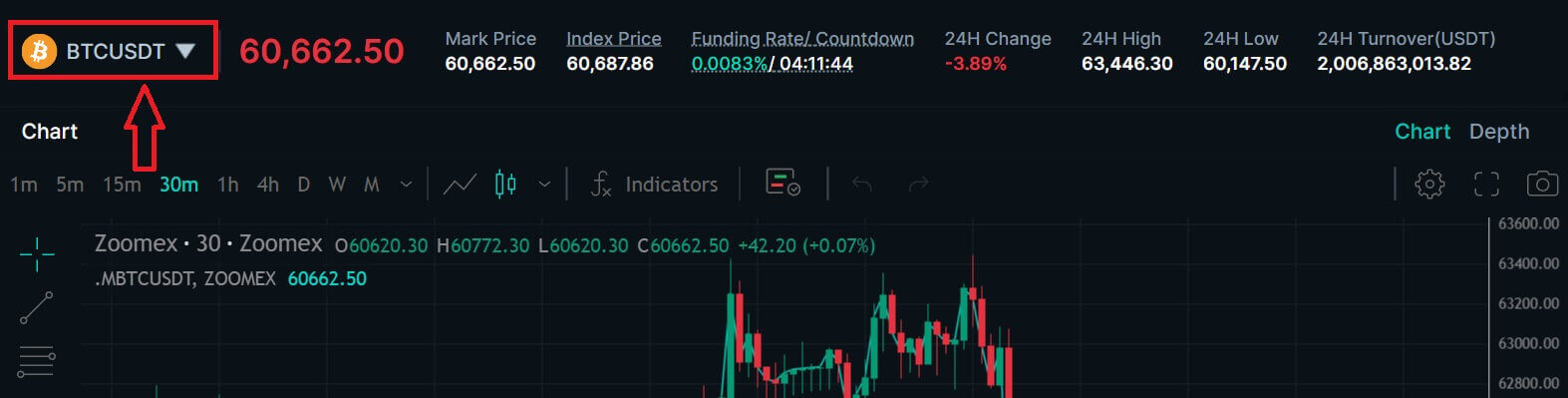
4. A list of trading pairs available will come up for you to choose below.
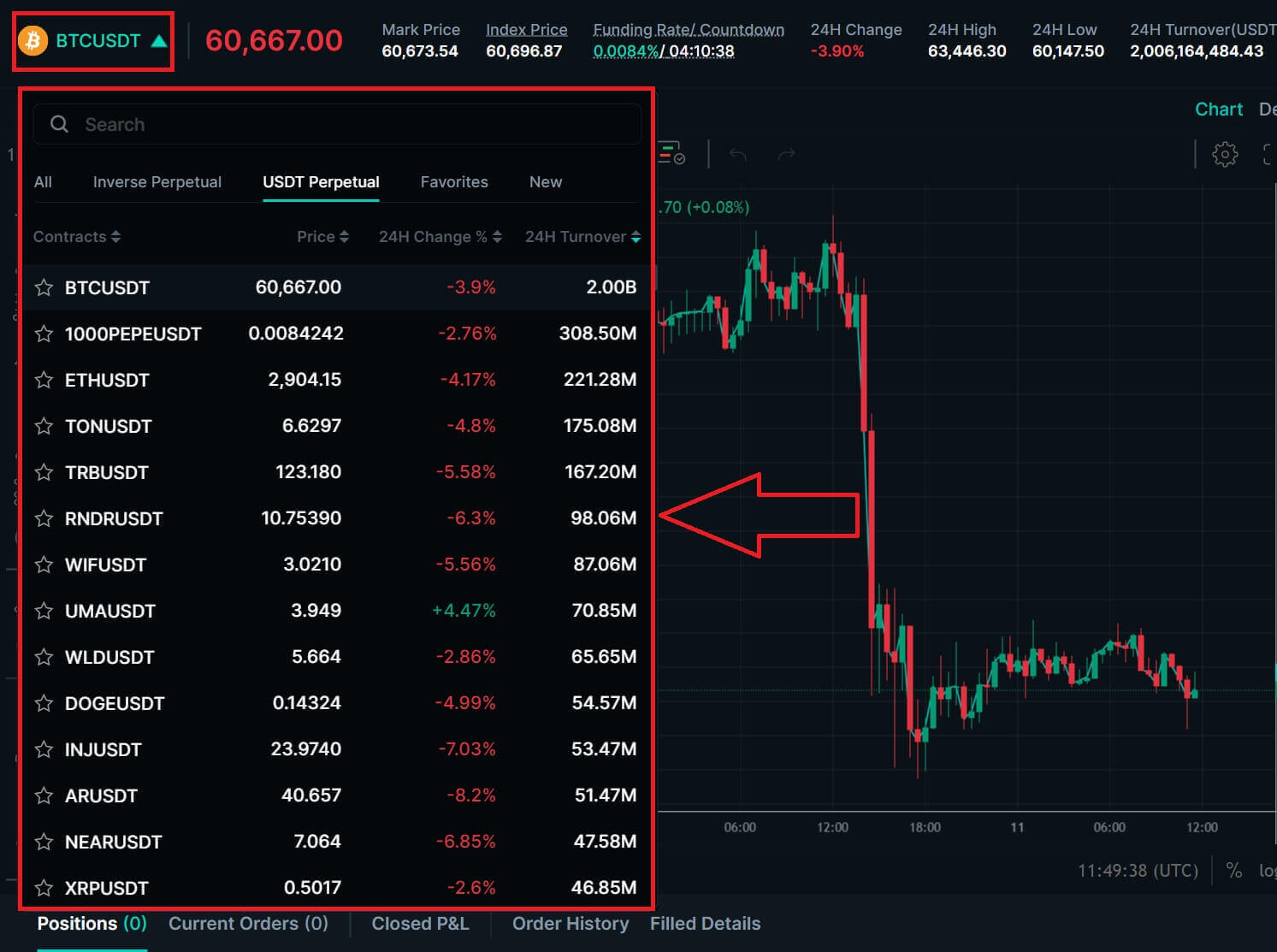 5. To open a position, users can choose between three options: Limit Order, Market price, and Conditional.
5. To open a position, users can choose between three options: Limit Order, Market price, and Conditional.
- Limit: A limit order is an order placed in the order book at a specific limit price. After placing a limit order, when the market price reaches the set limit price, the order will be matched to trade. Therefore, a limit order can be used to buy at a lower price or to sell at a higher price than the current market price. Please note: When the limit order is placed, the system does not accept buying at high prices and selling at low prices. If you buy at high prices and sell at low prices, the transaction will be executed immediately at the market price.
- Market: A market order is an order that trades at the current best price. It is executed against the previously placed limit order in the order book. When placing a market order, you will be charged a taker fee for it.
- Conditional Order: The trigger order sets a trigger price, and when the latest price reaches the trigger price set before, the order will be triggered to enter the order book.
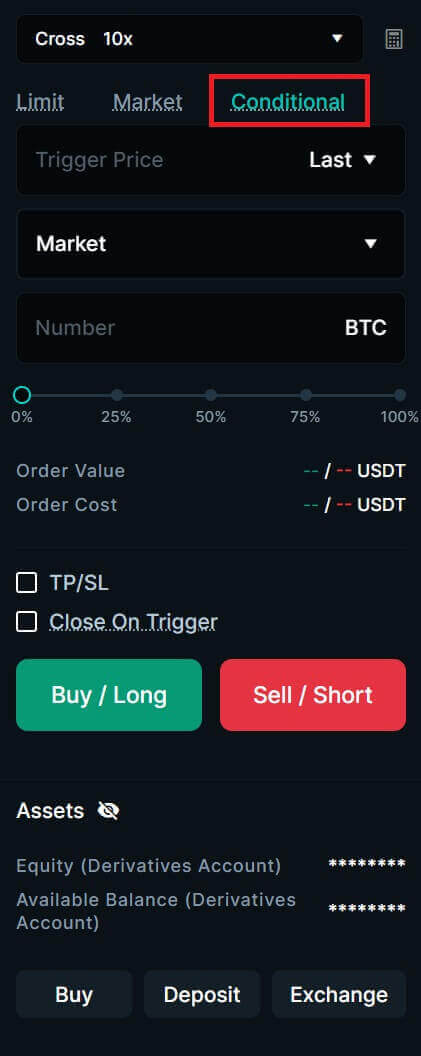
6. After choosing the order type, adjust your leverage for the transaction.
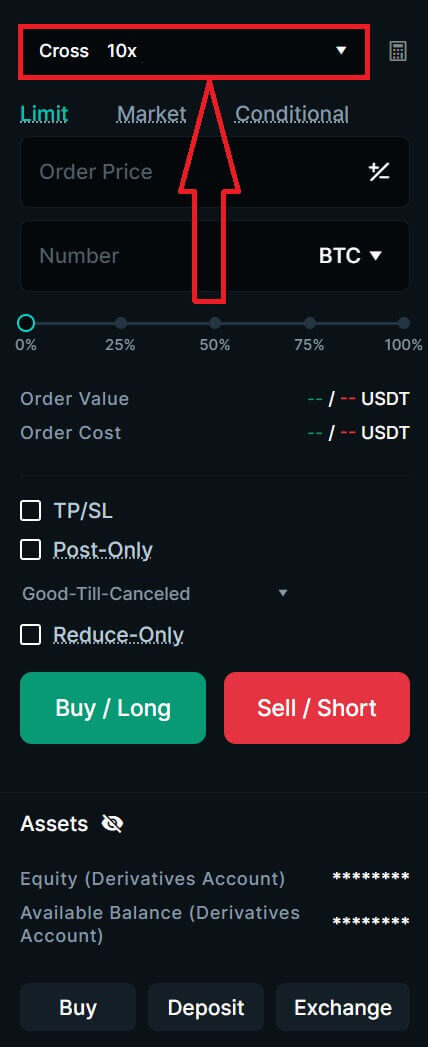
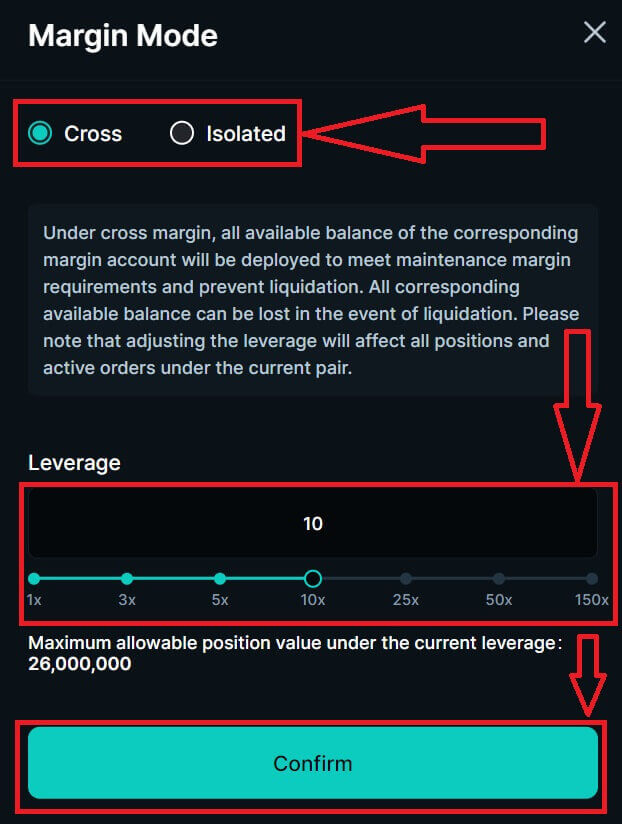
7. Choose your Margin Mode and adjust the Leverage, after that click on [Confirm] to keep the next step.
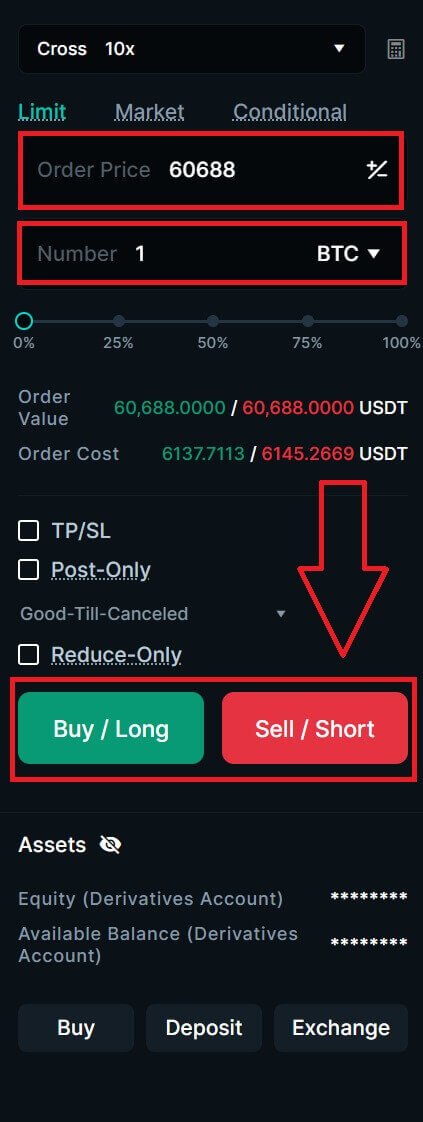
8. Type in the Number and the Order price (Limit order) of the coin that you want to do the order. In this example, I want to order 1 BTC for the 60688USDT limit price. After set up, click on [Buy/Long]/[Sell/Short] to execute the order.
9. After placing your order, view it under [Positions] at the bottom of the page. You can cancel orders before they’re filled. Once filled, find them under [Position]. To close your position, click [Close] under the Operation column.
How to Trade BTC/USDT Perpetual Futures on Zoomex (App)
1. Open the Zoomex app on your phone. Click on [Contract] to continue
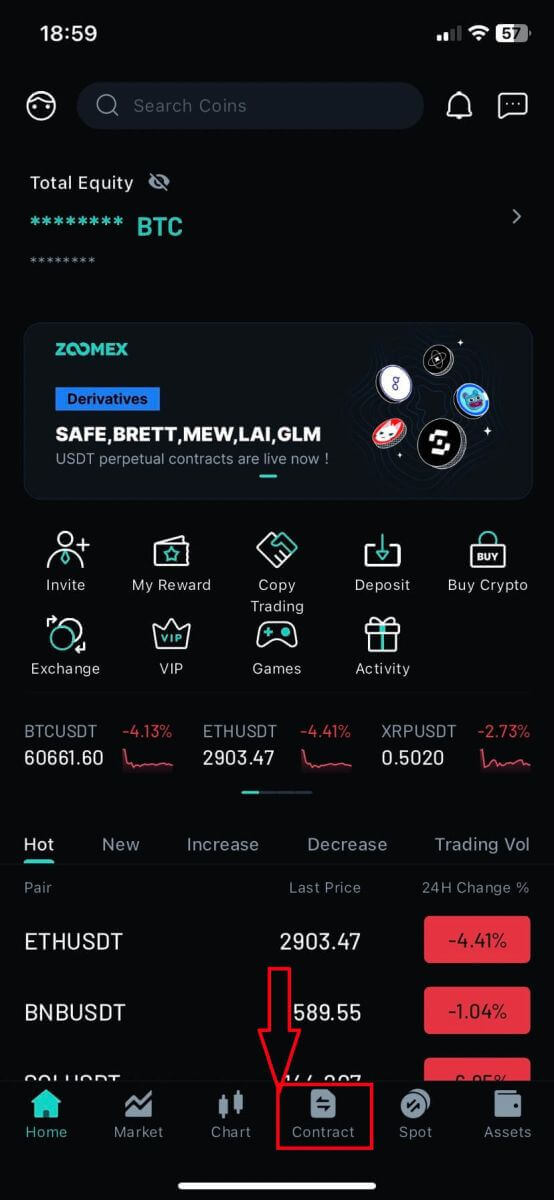
2. Here is the main page of Futures Trading.
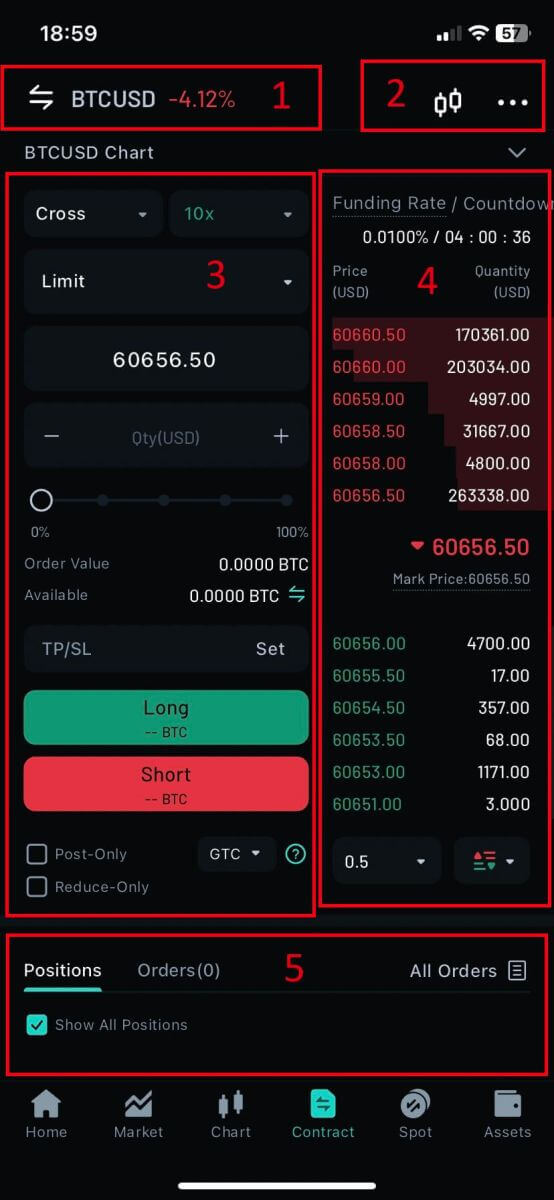
-
The trading volume of Spot Pairs in 24 hours:
This refers to the total volume of trading activity that has occurred within the last 24 hours for specific spot pairs (e.g., BTC/USD, ETH/BTC).
-
Candlestick Chart:
Candlestick charts are graphical representations of price movements over a specific period. They display opening, closing, and high, and low prices within the chosen timeframe, helping traders analyze price trends and patterns.
-
Buy/Sell Section:
This is where traders can place orders to buy or sell cryptocurrencies. It typically includes options for market orders (executed immediately at the current market price) and limit orders (executed at a specified price).
-
Order Book:
The order book displays a list of all open buy and sell orders for a particular cryptocurrency pair. It shows the current market depth and helps traders gauge supply and demand levels.
-
Current Orders/Order History/Trade History:
Traders can view their Current Order, Order History, and Trade History, including details such as entry price, exit price, profit/loss, and time of trade.
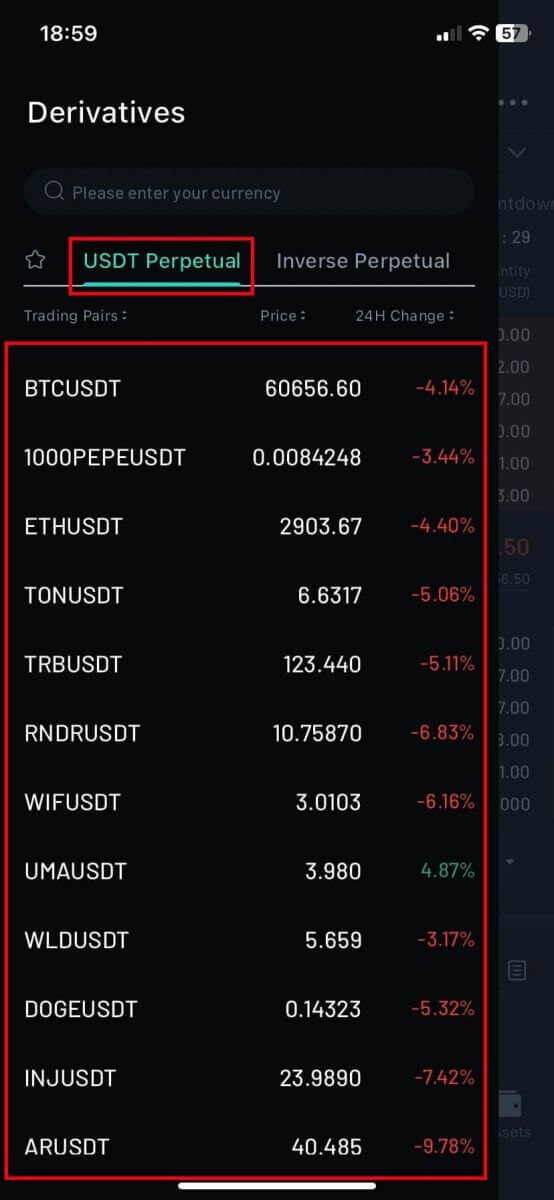
3. Choose the trading Pairs that you prefer to operate on the left crypto column.
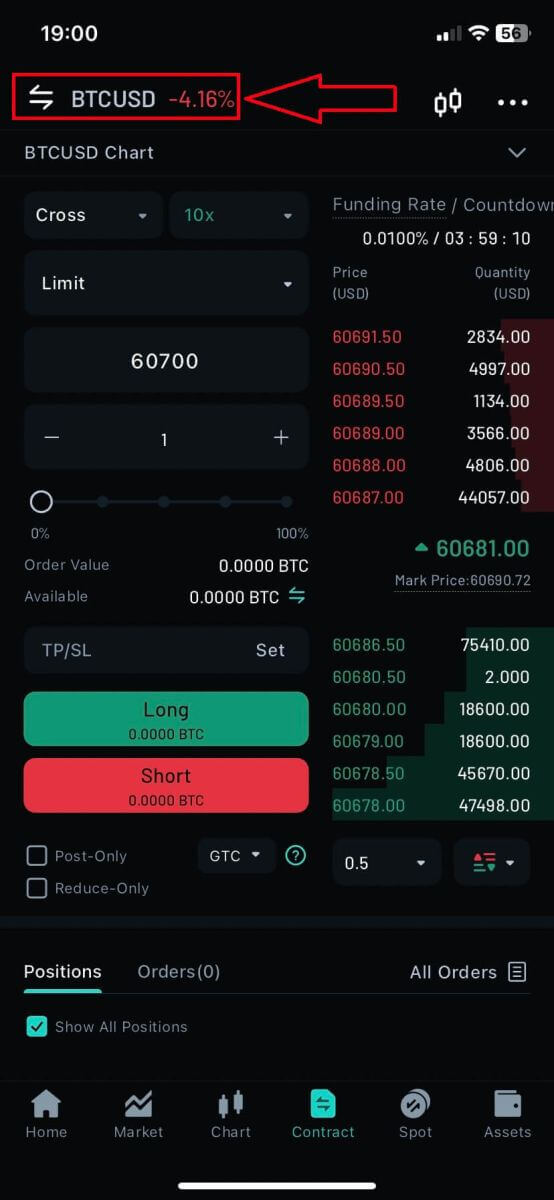
4. Tap on [Cross] to adjust the margin mode.
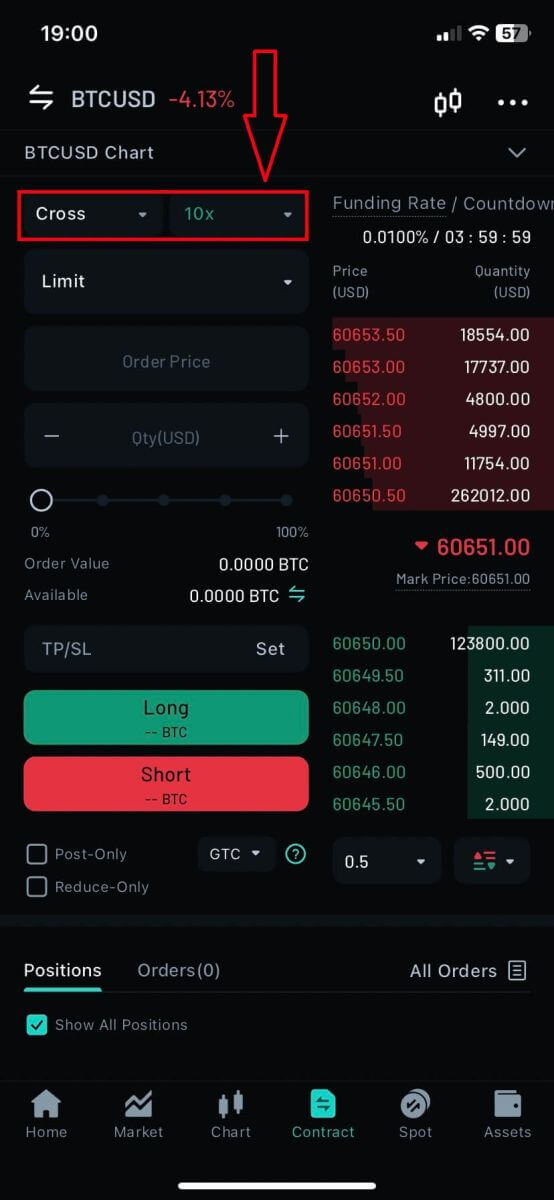
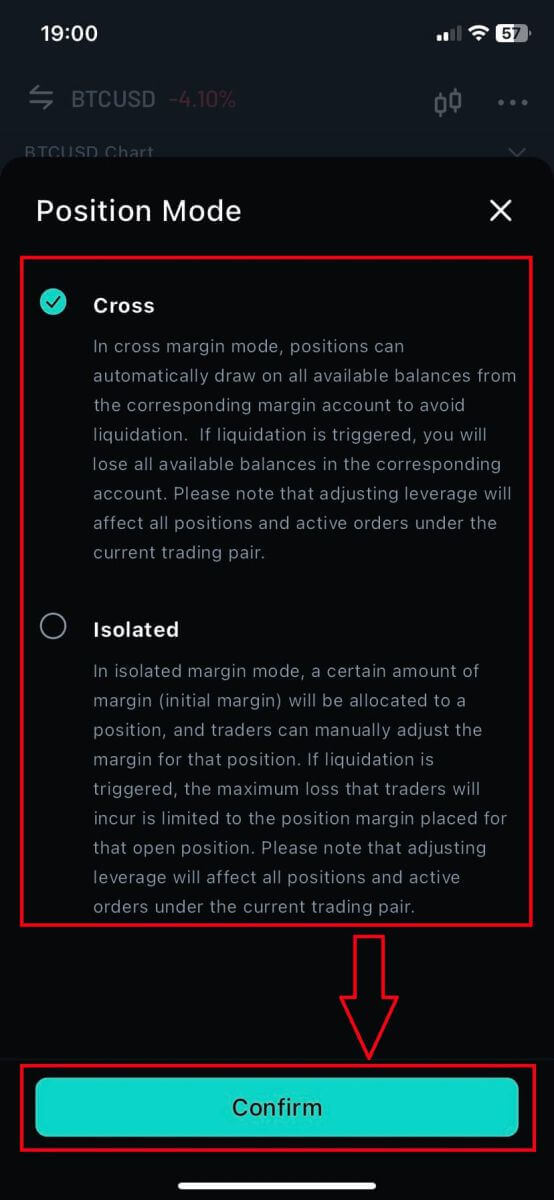
5. Choose the Position/Margin Mode then click on [Confirm] to finish.
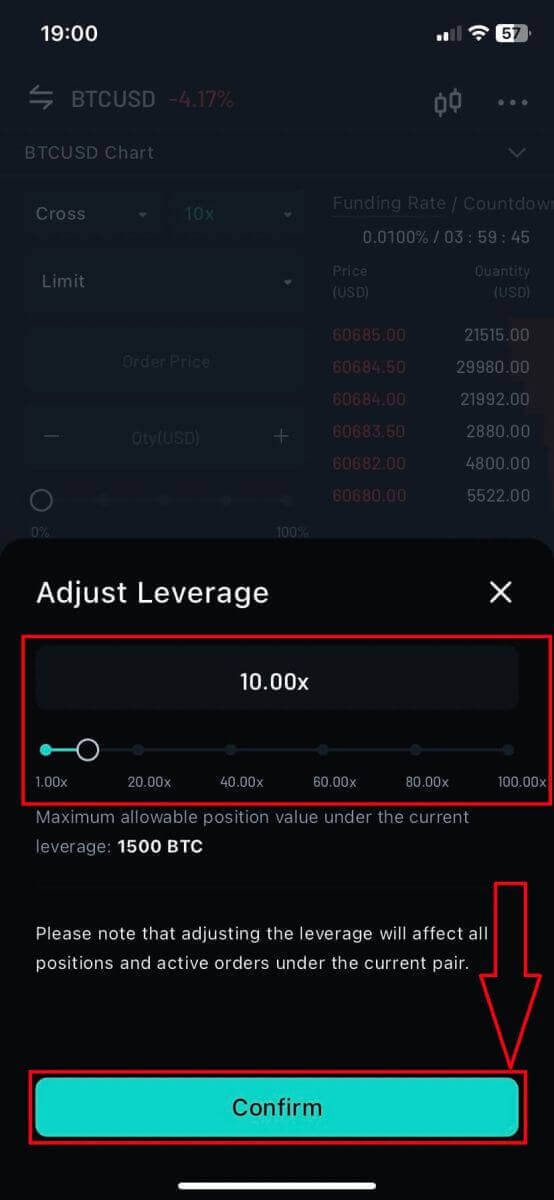
6. Same with the Leverage, adjust it and then click on [Confirm] to finish.
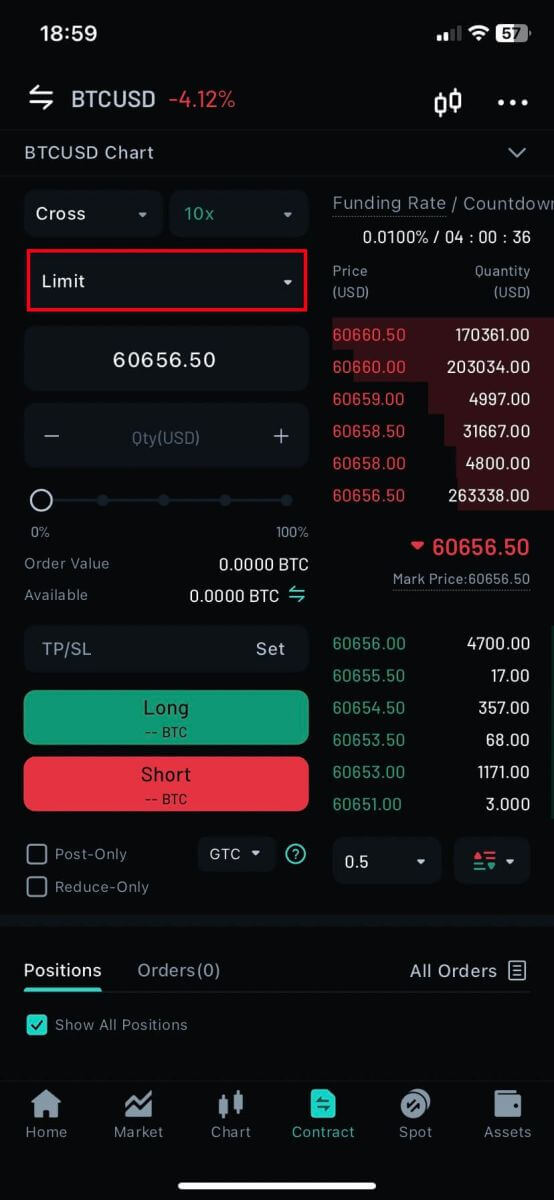
7. To open a position, users can choose between three options: Limit Order, Market price, and Conditional.
- Limit: A limit order is an order placed in the order book at a specific limit price. After placing a limit order, when the market price reaches the set limit price, the order will be matched to trade. Therefore, a limit order can be used to buy at a lower price or to sell at a higher price than the current market price. Please note: When the limit order is placed, the system does not accept buying at high prices and selling at low prices. If you buy at high prices and sell at low prices, the transaction will be executed immediately at the market price.
- Market: A market order is an order that trades at the current best price. It is executed against the previously placed limit order in the order book. When placing a market order, you will be charged a taker fee for it.
- Conditional Order: The trigger order sets a trigger price, and when the latest price reaches the trigger price set before, the order will be triggered to enter the order book.
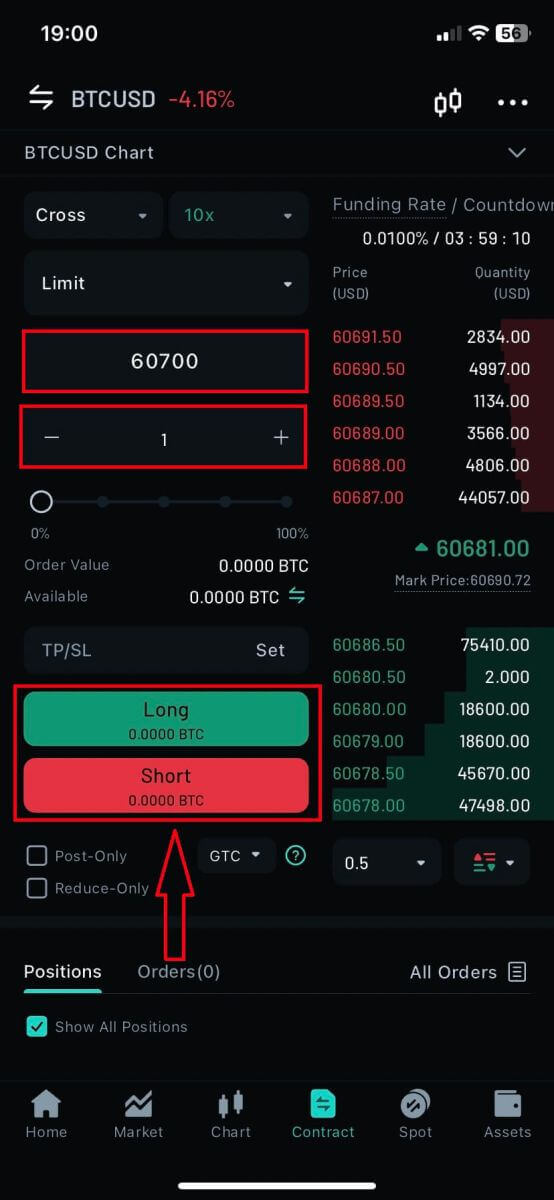
8. Type in the Number (Qty) and the Order price (Limit order) of the coin that you want to do the order. In this example, I want to order 1 BTC for the 60700 USDT limit price. After set up, click on [Buy/Long]/[Sell/Short] to execute the order.
9. After placing your order, view it under [Positions] at the bottom of the page. You can cancel orders before they’re filled. Once filled, find them under [Position]. To close your position, click [Close] under the Operation column.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How to change leverage
Locate the order placement zone on the right side of the trading page. Click on the ’Long’ or ’Short’ icons located on the top right corner of the order placement zone. A leverage must be manually keyed into the ’Long Lvg’ and ’Short Lvg’. Click on ’Confirm’ to proceed.
How to set up your time-in-force order strategy?
Locate the order placement zone on the right side of the trading page. The time-in-force function is only available to limit and conditional limit orders. Click on ’Good-Till-Cancelled’ and select your time-in-force order strategy from the pop-up menu. Proceed to successfully place the order. The system will execute the order based on the selected time-in-force order strategy.
How to place post-only orders?
Locate the order placement zone on the right side of the trading page. Post only function is only shown when placing limit or conditional limit orders. Enable it by checking the box as shown belowProceed to successfully place the order. The system will auto-cancel the order if it checks and determines that the order will be executed immediately.
Why Is The Displayed Order Cost Different For Buy Long And Sell Short Orders?
Inside the order zone, traders may notice that for the same contract quantity, the order cost may differ for a Buy Long and Sell Short direction. There are 2 reasons why.
1) The formula for calculating order cost
In this regard, traders can easily identify that the reason for the difference in order cost between a Buy Long and Sell Short order is due to the bankruptcy price used to calculate the fee to close.
For example BTCUSD 1000 Contract Quantity at USD 7500 entry price, 20x leverage for both Buy Long and Sell Short direction
Bankruptcy Price for Buy Long = 7500 x [20/(20+1)] = USD 7143
Bankruptcy Price for Sell Short = 7500 x [20/(20-1)] = USD 7894.50
Fee to close = ( Quantity / Bankruptcy Price ) x 0.06%
Note: The fee to close is only an amount of margin set aside by the system to allow the position to close at its theoretical worst case scenario (liquidation executed at bankruptcy price). This is not the absolute final amount that traders will always pay when closing the position. If traders close their position via Take Profit or Stop Loss and there are excess margin leftovers, they will be credited back to the user’s available balance.
2) The input of the order price in a limit order
a) When order price is placed at a price better than Last Traded Price (Buy Long = Lower, Sell Short = Higher)
-The system will only use the order price to calculate the fee to open, which in turn affects the overall order cost.
b) When order price is placed at a price worse than Last Traded Price (Buy Long = Higher, Sell Short = Lower)
-The system will use the best available market price based on the order book to calculate the fee to open, which in turn affects the overall order cost.
Differences Between Maker Orders and Taker Orders
One of the most common inquiries from traders is, “What are maker orders and taker orders?” Traders may notice that the taker fee is always higher than the maker fee. The chart below shows the difference between the two.
| Maker Orders | Taker Orders | |
| Definition | Orders that enter the order book and fill up the liquidity inside the order book before execution. | Orders that execute immediately by taking liquidity out from the order book. |
| Trading Fee | 0.02% | 0.06% |
| Order Placement Types | Limit Orders only | Can be either Market or Limit Orders |
How does this affect trading? Let’s look at the illustration below.
Using a BTCUSDT Perpetual Contract as an example:
| Trading Pair | BTCUSDT |
| Contract Size | 2 BTC |
| Trading Direction | Buy Long |
| Entry Price | 60,000 |
| Exit Price | 61,000 |
Trader A: Opening and closing position via two-way maker orders
| Fee to open | 2 × 60,000 × 0.02% = 24 USDT |
| Fee to close | 2 × 61,000 × 0.02% = 24.4 USDT |
| Position PL (excluding fees) | 2 × (61,000 − 60,000) = 2,000 USDT |
| Closed PL | 2000 − 24 − 24.4 = 1,951.60 USDT |
Trader B: Opening and closing position via two-way taker orders
| Fee to open | 2 × 60,000 × 0.06% = 72 USDT |
| Fee to close | 2 × 61,000 × 0.06% = 73.2 USDT |
| Position PL (excluding fees) | 2 × (61,000 − 60,000) = 2,000 USDT |
| Closed PL | 2000 − 72 − 73.2 = 1,854.80 USDT |
From the above illustration, we can see that Trader A pays a lower trading fee compared to Trader B.
In order to place a maker order, traders need to do the following:
・Use a Limit Order inside the order placement zone
・Select Post-Only
・Set your Limit Order price at a better price point compared to current market prices
Better price for Buy Long orders = Lower than best ask prices
Better price for Sell Short orders = Higher than best bid prices
If your Limit Orders are executed immediately, they will be considered as taker orders. Click here to find out more about why Limit Orders may unintentionally be executed immediately.
Notes:
— Closed PL records your position’s final profit and loss amounts after fees.
— Zoomex adopts the same maker-and-taker fee structure for all trading pairs on the platform.
What is funding rate?
Funding rate consists of two parts: Interest Rate and Premium Index.
Interest Rate (I)
- Interest Quote Index = The Interest Rate for borrowing the Quote currency
- Interest Base Index = The Interest Rate for borrowing the Base currency
- Funding Interval = 3 (Since funding occurs every 8 hours)
Interest Quote Index = 0.06%, Interest Base Index = 0.03%
Formula: The Interest Rate = (0.06%-0.03%)/3 = 0.01%.
Premium Index (P)
Perpetual contracts may trade at a premium or discount from the Mark Price. In this situation, a Premium Index will be used to raise or lower the next Funding Rate to be level consistent with where the contract is trading. On zoomex’s website, history records of Premium Indexes (.BTCUSDPI; Premium Index) can be found at the Index section under the ’Contracts’ tab.
Premium Index (P)=Max(0, Impact Bid Price - Mark Price) - Max(0, Mark Price - Impact Ask Price)Index Price+Funding Rate of Current Interval∗Time Until Next FundingFunding IntervalPremium Index (P)=Max(0, Impact Bid Price - Mark Price) - Max(0, Mark Price - Impact Ask Price)Index Price+Funding Rate of Current Interval∗Time Until Next FundingFunding IntervalFunding Rate (F)=Premium index (P) + clamp (Interest rate (I) - Premium index (P), 0.05%, -0.05%)Funding Rate (F)=Premium index (P) + clamp (Interest rate (I) - Premium index (P), 0.05%, -0.05%)
Impact Margin Notional is the notion available to trade with 0.1 BTC/2 ETH/200 EOS/ 2000 XRP/ 1000 DOT / 50,000 USDT worth of initial margin and is used to determine how deep in the order book to measure either the Impact Bid or Ask Price.
Funding Rate Calculation
zoomex calculates the Premium Index (P) and Interest Rate (I) every minute and then performs an 8-Hour Time-Weighted-Average-Price (TWAP) over the series of minute rates.
The Funding Rate is next calculated with the 8-Hour Interest Rate Component and the 8-Hour Premium / Discount Component. A +/-0.05% dampener is added.
Funding Rate (F) = Premium Index (P) + clamp(Interest Rate (I) - Premium Index (P), 0.05%, -0.05%)
Hence, if (I - P) is within +/-0.05% then F = P + (I - P) = I. In other words, the Funding Rate will equal the Interest Rate.
This calculated Funding Rate is then applied to a trader’s Position Value to determine the Funding Fee to be paid or received at the Funding Timestamp.
For the majority of contract pairs, funding fees are settled three times daily, precisely at 8:00 AM, 4:00 PM, and 12:00 AM UTC. Settlements occur promptly upon reaching these designated times.
Please note that certain contract pairs may have slightly different funding schedules, primarily influenced by market volatility. We recommend consistently checking the trading page for the most up-to-date and accurate information on these pairs.
Zoomex reserves the right to adjust the funding settlement times as needed to align with market demands. Such adjustments may occur without prior notice to users.
Funding Rate Limit
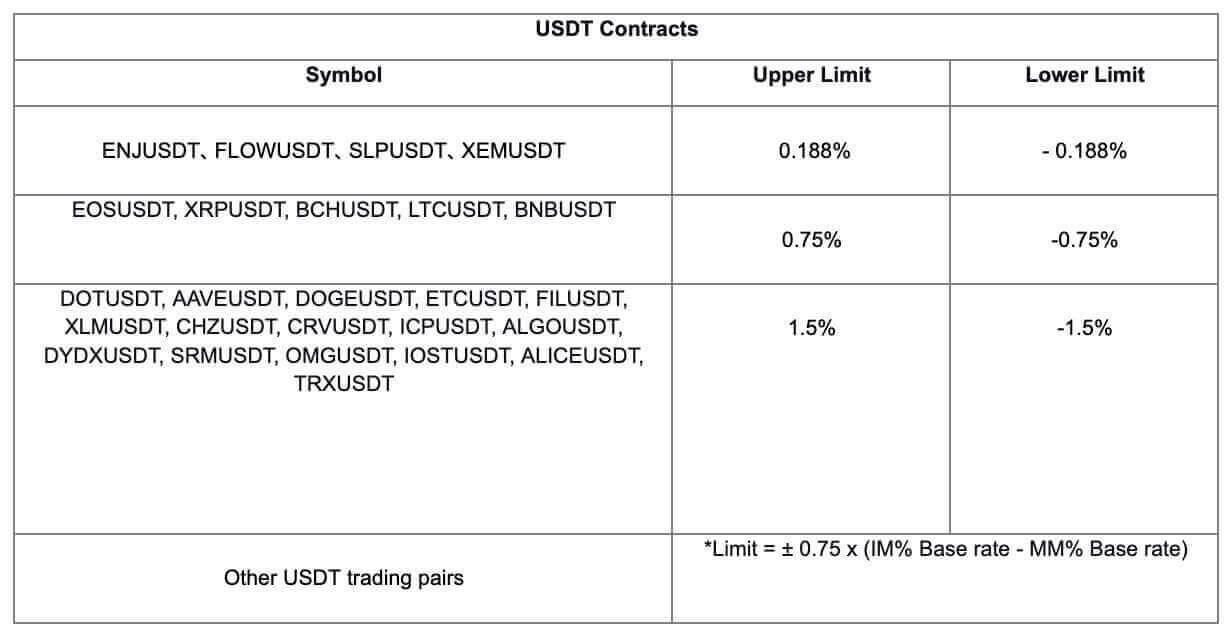
Traders may check on the funding rate, which will fluctuate in real time until the upcoming funding timestamp. The funding rate is not fixed, and is updated every minute, according to the Interest Rate and Premium Index, which affects the calculation of the funding rate until the end of the current funding interval.
Taker’s Fee and Maker’s Fee Calculation
Derivatives Trading
- Market Takers, who seek liquidity and take liquidity off the book immediately, will be charged a trading fee.
Inverse Contract
| Perpetual Contracts (Inverse) |
Highest Leverage | Maker’s Fee | Taker’s Fee |
|---|---|---|---|
| BTC/USD | 100x | 0.02% | 0.06% |
| ETH/USD | 100x | 0.02% | 0.06% |
| XRP/USD | 50x | 0.02% | 0.06% |
| EOS/USD | 50x | 0.02% | 0.06% |
Formula for Inverse Contract:
Trading Fee = Order Value x Trading Fee RateOrder value = Quantity / Executed Price
Trader A buy 10,000 BTCUSD contracts using Market order.
Trader B sell 10,000 BTCUSD contracts using Limit order.
Assuming that the execution price is 8,000 USD:
Taker fee for Trader A = 10,000/8,000 x 0.06% = 0.00075 BTC
fee for Trader B = 10,000/8,000 x 0.02% = 0.00025 BTC
USDT Contract
| Maker’s Fee | Taker’s Fee |
|---|---|
| 0.02% | 0.06% |
Formula for USDT Contract: Trading Fee = Order Value x Trading Fee Rate
Order value = Quantity x Executed Price
USDT Contract Example:
Trader A buy 10 BTC contract using Market order.
Trader B sell 10 BTC contract using Limit order.
Assuming that the execution price is 8000 USDT:
Taker’s Fee for Trader A = 10 x 8000 x 0.06% = 48 USDT
fee for Trader B = 10 x 8000 x 0.02% = 16 USDT
Does Leverage Affect Your Unrealized PL?
The answer is no. On Zoomex, the main function of applying leverage is to determine the initial margin rate required to open your position, and selecting higher leverage does not directly amplify your profits.
For example, Trader A opens a 20,000 Qty Buy Long inverse perpetual BTCUSD position on Zoomex. Refer to the table below to understand the relationship between leverage and initial margin.
| Leverage | Position Qty (1 Qty = 1 USD) | Initial Margin Rate (1/Leverage) | Initial Margin Amount (BTCUSD) |
| 1x | 20,000 USD | (1/1) = 100% | 20,000 USD worth in BTC |
| 2x | 20,000 USD | (1/2) = 50% | 10,000 USD worth in BTC |
| 5x | 20,000 USD | (1/5) = 20% | 4,000 USD worth in BTC |
| 10x | 20,000 USD | (1/10) = 10% | 2,000 USD worth in BTC |
| 50x | 20,000 USD | (1/50) = 2% | 400 USD worth in BTC |
| 100x | 20,000 USD | (1/100) = 1% | 200 USD worth in BTC |
Note:
1) Position Qty is the same regardless of leverage applied
2) Leverage determines the initial margin rate.
- The higher the leverage, the lower the initial margin rate and thus a lower initial margin amount.
3) Initial margin amount is calculated by taking position qty multiply by initial margin rate.
Next, Trader A is considering closing his 20,000 Qty Buy Long position at USD 60,000. Assuming that the average entry price of the position was recorded at USD 55,000. Refer to the table below shows the relationship between leverage, Unrealized PL (profit and loss) and Unrealized PL%
| Leverage | Position Qty (1 Qty = 1 USD) | Entry Price | Exit Price | Initial Margin Amount based on entry price of USD 55,000 (A) | Unrealized PL based on exit price of USD 60,000 (B) | Unrealized PL%(B) / (A) |
| 1x | 20,000 USD | 55,000 | 60,000 | 20,000/(55,000 x 1) = 0.36363636 BTC | 0.03030303 BTC | 8.33% |
| 2x | 20,000 USD | 55,000 | 60,000 | 20,000/(55,000 x 2) = 0.18181818 BTC | 0.03030303 BTC | 16.66% |
| 5x | 20,000 USD | 55,000 | 60,000 | 20,000/(55,000 x 5) = 0.07272727 BTC | 0.03030303 BTC | 41.66% |
| 10x | 20,000 USD | 55,000 | 60,000 | 20,000/(55,000 x 10) = 0.03636363 BTC | 0.03030303 BTC | 83.33% |
| 50x | 20,000 USD | 55,000 | 60,000 | 20,000/(55,000 x 50) = 0.00727272 BTC | 0.03030303 BTC | 416.66% |
| 100x | 20,000 USD | 55,000 | 60,000 | 20,000/(55,000 x 100) = 0.00363636 BTC | 0.03030303 BTC | 833.33% |
Note:
1) Notice that despite different leverages being applied for the same position qty, the resulting Unrealized PL based on exit price of USD 60,000 remains constant at 0.03030303 BTC.
- Therefore, higher leverage does not equal to higher PL.
2) Unrealized PL is calculated by taking into consideration the following variables: Position Qty, Entry Price and Exit Price
- The higher the Position Qty = the greater the PL
- The larger the price difference between entry price and exit price = the greater the Unrealized PL
3) Unrealized PL% is calculated by taking the Position Unrealized PL / Initial Margin Amount (B) / (A).
- The higher the leverage, the lower the initial margin amount (A), the higher the Unrealized PL%
- For more info, please refer to the articles below
4) The Unrealized PL and PL% illustration above does not take into consideration any trading fees or funding fees. For more info, please refer to the following articles
- Trading Fee Structure
- Funding fee calculation
- Why Did My Closed PL Record A Loss Despite The Position Showing a Green Unrealized Profit?